It’s fascinating how the world of energy can be swiftly disrupted by innovation. Not long ago, General Electric introduced a cutting-edge combined cycle methane-fired turbine in Menifee, California. This technology harnesses the waste heat from burning methane, enhancing its efficiency in generating electricity. While it was anticipated to operate for several decades, today, a dramatic shift has occurred with the introduction of grid-scale battery storage, rendering it a relic of the past.
The Mechanisms of Combined Cycle Technology
GE’s combined cycle turbine was an intricate dance of air, fuel, and fire. Air compressed and mixed with fuel reaches scorching temperatures before propelling turbine blades, and the resulting momentum converts into electricity through a generator. To recapture emitted heat, a heat recovery steam generator harvests exhaust warmth, creating steam that drives an additional turbine, further amplifying electricity production.
Nova: A Beacon of Modern Energy Storage
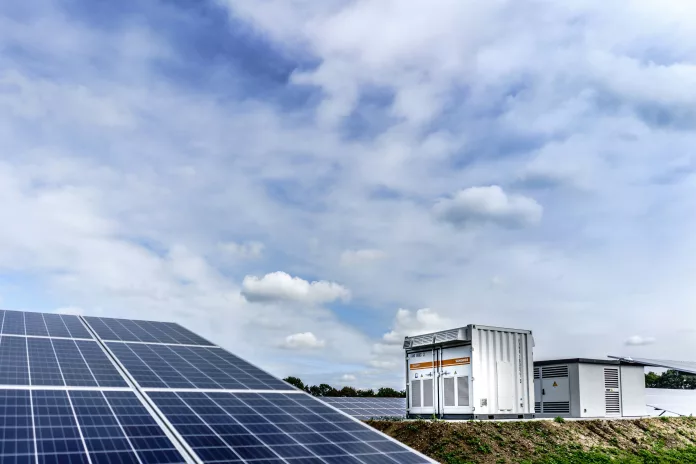
Replaced by a behemoth $1 billion battery storage facility dubbed Nova, the site of the old gas-fired power plant has embraced the future. Mortenson is at the helm of this project for Calpine, and upon completion, Nova will boast a storage capacity of 680 MW, equipping it to supply the grid for four hours – that’s an impressive 2720 MWh of energy ready to fulfill late afternoon and early evening demands.
Why Grid-Scale Storage Is the Future
The combined cycle plants, now outmoded, fell victim to the rise of solar power, which thrives under the Californian sun. Storing the afternoon’s solar bounty and redistributing it as the day wanes means a grid powered by emissions-free electricity. Contrastingly, gas plants take an unwieldy 12 hours to initialize, an impractical and costly endeavor just to produce energy for a few peak hours.
Mayor Bill Zimmerman of Menifee lauded the efficiency and operational simplicity of the incoming Nova project compared to the cumbersome gas-fired predecessor. Calpine, a pioneer in battery technology, now strides forward with Nova setting a benchmark in storage capacity and confidently predicts a surge of installations across the United States.
Impressive Scale and Speed of Deployment
Nova is not just another project; it’s an assembly of 1,096 battery containers, housing over 26,000 battery modules and 3 million cells provided by BYD. This powerhouse can energize 680,000 homes for up to four hours. And unlike conventional power plants, this mega battery sprung up rapidly, with construction initiating just last August and reaching substantial operational milestones by the coming summer.
Menifee was an ideal location, particularly due to existing grid connections. The facility promises rapid response times, essential for integrating unpredictable renewable sources. Calpine’s decision was a strategic response to the evolving energy landscape, where utility companies anticipate a surge in demand due to a greater reliance on electric vehicles and heat pumps.
Regulatory Tailwinds Boosting Battery Adoption
Modularity is key to the speed of grid-scale battery construction. The Menifee battery consists of interchangeable parts, each connecting to standardized substations. California’s forward-thinking energy storage mandate paved the way for a methodical approach toward realizing a market buttressed by strong solar generation capabilities.
Despite the rapid growth, methane as an electricity source persists, but state policies increasingly favor battery expansion, encouraged by declining battery costs and established business models for energy storage. Calpine’s venture into battery technology, influenced by these broader trends, demonstrates a commitment to a cleaner grid and dispatchable energy resources.
Learning from Competition and Past Innovations
Calpine’s leap into large-scale battery storage has been emboldened by the experiences of its competitors such as Vistra, which previously constructed a massive battery facility. However, issues like fires at the Vistra project allowed Calpine to innovate fire safety measures for Nova, making it even more reliable. Mortenson’s accumulated expertise from similar projects enabled a swift and effective construction process.
Considering the Bigger Picture
Calpine’s Nova project stands out in both scale and efficiency. The economic benefits of stable electricity prices, in contrast to the volatile costs of gas, make battery storage increasingly attractive. Yet, the integral role of policy in shaping the energy sector is evident, as fossil fuel-heavy strategies adopted by some states may lead to higher costs for consumers in the long run.
Despite the convenience and economic rationale, the transition towards battery storage faces hurdles in regions where policy favors fossil fuels. Nevertheless, the path charted by technological advancement and meticulous regulation in places like California illuminates a possible future where energy storage takes center stage in supporting a sustainable power grid.