As the electric vehicle (EV) landscape evolves, breakthroughs continue to capture the imagination of enthusiasts. Key areas of advancement include optimizations in regenerative braking, ongoing refinement of battery tech, and the rise of connected transport networks. A key growth aspect of the EV sector is the rapid development of innovative charging solutions, especially the introduction of wireless charging technology, which could soon see electric cars powered by the roads they drive on.
The Detroit Electric Mile: A Glimpse into the Future of EV Charging
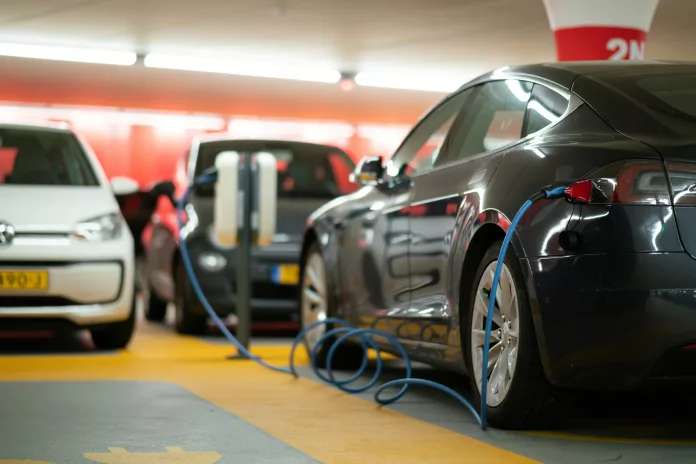
The unveiling of a pioneering stretch of pavement on 14th Street in Detroit marks an important milestone in EV infrastructure. This section of road is capable of wirelessly charging EVs as they pass over it—heralding the dawn of the nation’s first wireless charging public roadway for electric vehicles.
This endeavor is part of a cutting-edge pilot program where the Michigan Department of Transportation has joined forces with Electreon, an Israeli tech firm. Their five-year collaboration aims to install and test in-road inductive charging coils that enable EVs with compatible receivers to charge while stationary or in motion, offering a seamless wireless power solution.
The technology operates by activating coils embedded in the pavement to generate a magnetic field that transfers energy to an EV’s battery. The system remains dormant until a vehicle with the proper equipment approaches, ensuring the road remains safe for all users, including pedestrians and animals.
How Does Inductive Road Charging Function?
Explored in detail in the journal Energies, wireless road charging involves a mechanism where galvanic isolation allows for an energy transfer across loosely coupled coils through magnetic induction. The process begins by converting AC power into a high-frequency current that energizes the primary coil beneath the road’s surface. The secondary coil within the vehicle then receives this energy, charging the battery as the EV travels along the smart road.
Implementing this Dynamic Wireless Charging (DWC) system is challenging, but holds vast potential. Researchers underscore its ability to alleviate limited range anxieties and suggest it could lead to lighter, more cost-effective EV batteries due to the continuous charging possibility.
Bringing Innovations to Life: Michigan Central and Electreon’s Partnership
Michigan Central, an institution focused on transforming urban transport, and Detroit’s local authorities have come together to spearhead this electrified road project. Their mutual goal is to refine the technology for public use. Michigan Central operates in Detroit’s innovation district, bridging Corktown and Southwest Detroit—regions ripe for such avant-garde developments.
As progress continues, Michigan’s DOT plans to introduce more electric avenues, like reconstructing portions of Michigan Avenue to incorporate wireless charging technology. The technology has already proven reliable across diverse temperatures, maintaining functionality even under harsh winter conditions.
Electreon is at the forefront of this technological leap, engaged in similar initiatives across the globe. The company is invested in lowering the complexity and cost barriers to EV fleet adoption, offering innovative financing models like Charging as a Service (CaaS) to ease the transition for organizations.
With a vision firmly set on fostering an emission-free mobility future, Stefan Tongur, Electreon’s VP of Business Development, sees the project as a gateway to mainstreaming EVs. Enabling charging capabilities for multiple vehicles simultaneously could shift industry standards towards smaller, more efficient batteries—ultimately promoting more affordable and lightweight electric vehicles.
Electreon’s pilot aims to demonstrate the practicality and efficiency of wireless dynamic charging for a variety of vehicles and use cases. It also aspires to catalyze larger Electric Road Systems throughout the US, whilst fostering partnerships that could serve as a framework for future innovation and infrastructure growth.