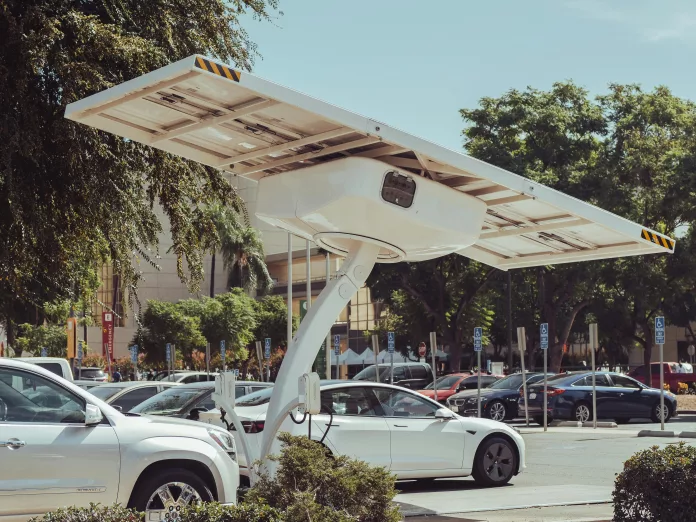
In a significant move to propel the adoption of electric vehicle (EV) infrastructure, the US Treasury Department has unveiled new guidance delineating the prerequisites for tax credit qualification for both individuals and business entities investing in EV chargers. This comes as a boon for those keen on integrating sustainable energy solutions into their lives and operations.
Key Features of the Alternative Fuel Vehicle Refueling Property Credit
Since the Inflation Reduction Act took hold in August 2022, it has allowed for a lucrative tax incentive amounting to 30% of the outlay for qualified EV charging infrastructure. Known more formally as the Alternative Fuel Vehicle Refueling Property Credit, significant changes have been made. The modified structure now assigns the tax credit to each specific EV charging device rather than imposing it on the whole installation site.
Individuals can now harness a capped credit of $1,000 for residential EV charger installations, while business properties enjoy an elevated limit, rising from $30,000 to an impressive $100,000 strength. This change has been in practice from January 1, 2023, marking a significant expansion of the credit’s reach. Applications for the credit are processed using IRS Form 8911, and a direct pay option is available for eligible entities such as governmental bodies and non-profit organizations, allowing them to invest beneficially in EV infrastructure.
Qualification Criteria: The Importance of Location
The IRS has issued updated guidance emphasizing the importance of location for eligibility. To be considered for the 30C EV charging tax credit, the charging station must be sited within an “eligible census tract.” This essentially refers to areas categorized either as low-income communities or those situated outside urban zones as designated by the IRS.
Further emphasizing the broad applicability of the credit, a statement from the White House pointed out that these measures ensure around two-thirds of Americans can benefit from the Inflation Reduction Act’s 30C EV charging tax credit. Aiding in discerning eligibility, the US Department of Energy, with the assistance of Argonne National Laboratory, has developed a convenient mapping tool. Although not recognized formally as IRS guidance and similarly not this article, this tool is instrumental in guiding potential applicants. However, it is advised to seek a tax professional’s input when filing.
The Role of the 30C Tax Credit in Expanding EV Infrastructure
Albert Gore III, speaking on behalf of the Zero Emission Transportation Association (ZETA), underscored the significance of the 30C tax credit as the principal stimulant for EV charging infrastructure deployment. With an existing national network of 170,000 publicly accessible EV chargers, the US sets its sights on a grand target—installing a colossal 500,000 public chargers by 2030. Achieving such an ambitious milestone heavily leans on the effective execution of the 30C tax incentive.
As the nation gradually transitions toward electric vehicles, these incentives and resources are poised to play critical roles in shaping a more sustainable and environmentally-friendly transportation ecosystem.