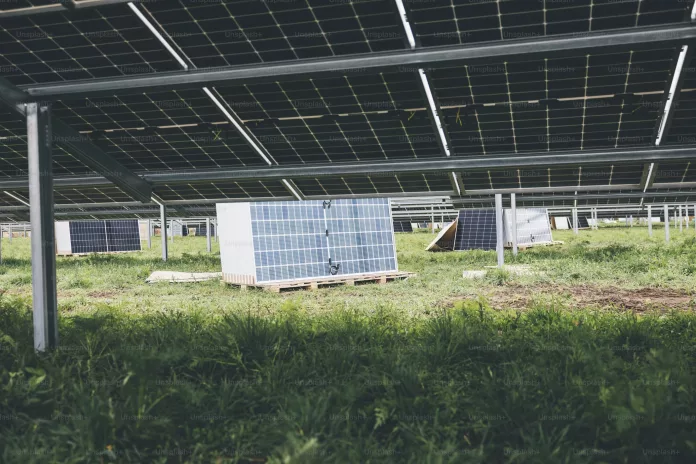
Amidst the complex relationship between renewable energy and agriculture, a German study delves into what motivates farmers to consider agrivoltaics—a fusion of crop cultivation and photovoltaic power generation—as a viable option. The fascination with combining these two elements has been heightened by the escalating threats agriculture faces due to the deleterious effects of climate change, such as floods, droughts, and wildfires, driven by fossil fuel byproducts. Contrary to the clamor propagated by the fossil fuel sector that aims to cast renewables as detrimental to farming, the study conducted by the esteemed Fraunhofer ISE in Germany seeks to address the actual concerns and attitudes of the farming community.
Deciphering Farmers’ Willingness for Agrivoltaic Adoption
In the upcoming publication in Applied Energy, set for May 2024, German researchers presented an online survey canvassing the views of 214 farmers which took place in February 2023. They employed factor analysis and binary logistic regression to dissect the disposition of farmers towards agrivoltaics. Astonishingly, a hefty 72.4% expressed openness to utilizing such systems. Dominant factors swaying their decision included the perceived usefulness of agrivoltaics, the influence of societal norms, and the innovativeness of the individual farmer. The promise of an additional revenue stream and prospective farm development were particularly enticing benefits for farmers; however, they also recognize bureaucratic intricacies and regulatory uncertainties as potential roadblocks to adopting the technology.
Influential Factors Encouraging Farmers Towards Agrivoltaics
The research identified a suite of economic and cultural factors prompting farmers to consider agrivoltaic systems. Among these factors, the stability and predictability of income from solar installations stood out, providing a compelling contrast to the unpredictable nature of traditional farming. Informational sources on agrivoltaics such as trade newspapers, agricultural consultants, and farmers’ associations were deemed reliable by the respondents, who showed less regard for radio, television, and social media. The study further noted the diversity in farming operations, highlighting that the design of agrivoltaic systems must be tailored to meet varying farm-specific needs and circumstances.
Farmers’ Concerns About Implementing Agrivoltaics
Despite a healthy interest in agrivoltaics among German farmers, the study uncovered that hesitancy is less about distrust in the technology and more about the cumbersome regulatory processes required for implementation. Interestingly, the research found that farmers also place value on the role agrivoltaics might play in their social settings and the broader environmental responsibility, though these aspects require additional inquiry. To overcome barriers, the study urges further exploration and actions to eliminate bureaucratic challenges, increase societal acceptance, and provide tangible evidence for the protective and synergistic attributes of agrivoltaics in agriculture.
The Bigger Picture for Farming and Renewable Energy
Farming endures as a challenging profession, susceptible to countless uncontrollable factors. Climate change, with its resulting extreme weather and economic implications, only exacerbates those challenges. This study demonstrates that farmers prioritize tangible, science-based solutions over empty rhetoric to thrive in their profession. Embracing agrivoltaics not only reflects adaptive innovation in farming but also underlines the shared destiny of agriculture and renewable energy in securing a sustainable future for both the environment and the farming communities.